Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hayano, Akira
Genshiryoku Bakkuendo Kenkyu (CD-ROM), 31(2), p.134 - 139, 2024/12
In the design and construction of a repository for high-level radioactive waste, it is considered to set criteria for the rational locating of disposal tunnels and holes, taking into account the effects of faults and fractures distributed in the host rock at the tunnel to pit scale and excavation damaged zones (EDZs) that occur after tunnel excavation on the workability of the disposal tunnels and the long-term stability of the engineered barriers. In addition, tunnel sealing technologies such as tunnel backfilling and hydraulic plugs will be considered to prevent short-circuit flow of radionuclides through the excavated tunnels and the surrounding EDZs. In Task B of the HIP, we will attempt to establish criteria for the layout of disposal tunnels and holes, and the systematic integration of technical options related to the design, construction, operation and closure of the repository, using the investigation and construction at the Horonobe URL for Neogene sedimentary rocks as a case study. Based on information provided by the participating organisations and existing case studies from Japan and overseas, the current focus is on the reduction of the mechanical strength of the rock mass, the effects of water inflow on disposal tunnels and holes, or the effects on engineered barriers, in relation to the locating of disposal tunnels and boreholes and the emplacement of engineered barriers, and is currently working on analyses to predict features associated with these. Investigation, construction and testing of the 500 m niches No. 8 and No. 9 to confirm the validity of these predictions, and full-scale tunnel backfilling and hydraulic plug installation test in the 350 m Niche No. 6, will be carried out in Phase 2 of the HIP.
Matsuda, Shinzaburo
IEEE Transactions on Plasma Science, 32(2), p.749 - 756, 2004/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.00(Physics, Fluids & Plasmas)no abstracts in English
Committee of the Halden Joint Research Programme
JAERI-Tech 2004-023, 38 Pages, 2004/03
JAERI has performed cooperative researches with several Japanese organizations utilizing the Halden Boiling Heavy Water Reactor(HBWR) which is located at Halden in Norway. These researches are carried out based on the contracts of the cooperative researches, which are revised every three years, in accordance with the renewal of the participation of JAERI to the OECD Halden Reactor Project. This report summarizes the objectives, contents and the outlines of the achievements of the cooperative researches during the three years from 2000 January to 2002 December. During the period, seven cooperative researches had been carried out. Two of them had been completed and other five researches have been continued to the next three years period. Most of them are irradiation test researches of advanced fuel and cladding in order to prepare the higher burnup utilization and introduction of LWR fuel and MOX fuel in LWRs of Japan.
Yamaguchi, Yasuhiro; Hirayama, Hideo*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(Suppl.4), p.498 - 501, 2004/03
JAERI-Universities Joint Research Project has been carried out to study the radiation safety in high-energy proton accelerator facilities since 2000. Ten groups from 2 research institutes and 5 universities joined in the project to tackle 3 major subjects below, using a quasi-monoenergetic neutron field at TIARA facility of JAERI. The groups had annual meetings to discuss the plan and progress of the studies and exchange their views for effective cooperation. (1)Studies on basic physical data necessary for neutron dosimetry. (2)Development of neutron monitors and dosimeters for several tens MeV region. (3)Studies on formation of radioactive aerosols and gases for internal dosimetry.
Nakano, Tomohide; Fujimoto, Takashi*; Goto, Motoshi*; Hatayama, Akiyoshi*; Kado, Shinichiro*; Kato, Takako*; Kimura, Mineo*; Kubo, Hirotaka; Murakami, Izumi*; Ono, Noriyasu*; et al.
Annual Report of National Institute for Fusion Science; April 2003 - March 2004, P. 414, 2003/10
no abstracts in English
JNC TN9440 2000-008, 79 Pages, 2000/08
This report summarizes the operating and irradiatlon data of the experimental reactor "JOYO" 35th cycle. Irradiation tests in the 35th cycle are as follows: (1)C-type irradiation rig (C4F) (a)High burnup performance test of advanced austenitic stainless steel cladding fuel pins (in collaboration with France) (2)C-type irradiation rig (C6D) (a)Large diameter fuel pins irradiation tests (3)Core Materials Irradiation Rig (CMIR-5) (a)Cladding tube materials irradiation tests for "MONJU" (4)Structure Materials Irradiation Rigs (SMIR) (a)Decision of material design base standard of structure materials for prototype reactor and large scale reactor (5)Upper core structure irradiation Plug Rig (UPR-1-5) (a)Upper core neutron spectrum effect and accelerated irradiation effect (6)SurVeillance un-instrument Irradiation Rig (SVIR) (a)Confimation of surveillance irradiation condition for "JOYO" (b)Material irradiation tests (based on a contract with universities) The maximum burnup driver assembly "PFD253" reached 67,600 MWd/t (pin average).
Sugino, Kazuteru; Iwai, Takehiko*;
JNC TN9400 2000-098, 182 Pages, 2000/07
In order to support the Russian excess weapons plutonium disposition, the international collaboration has been started between Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC) and Russian Institute of Physics and Power Engineering (IPPE). In the frame of the collaboration, JNC has carried out analyses on the BFS-62 assemblies that are constructed in the fast reactor critical experimental facility BFS-2 of IPPE. This report summarizes an experimental analysis on the BFS-62-1 assembly, which is the first core of the BFS-62 series. The core contains the enriched U0 fuel surrounded by the U0
fuel surrounded by the U0 blanket. The standard analytical method for fast reactors has been applied, which was used for the JUPITER and other experimental analyses. Due to the lack of the analytical data the 2D RZ core calculation was mainly used. The 3D XYZ core calculation was applied only for the preliminary evaluation. Further in terms of the utilization of the BFS experimental analysis data for the standard data base for FBR core design, consistency evaluation with JUPITER experimental analysis data has been performed using the cross-section adjustment method. As the result of analyses, good agreement was obtained between calculations and experiments for the criticality and the reaction rate ratio. However, it was found that accurate evaluation of the reaction rate distribution was impossible without exact consideration of the arrangement of the two types of sodium (with and without hydrogen impurity), which can be accommodated by the 3D core analysis, thus it was essentia1. In addition, it was clarifie that there was a room for an improvement of the result on the reaction rate distribution in the blanket and shielding regions. The application of the 3D core calculation improved the result on the control rod worth because 3D core model can more exactly consider the shape of the control rod. Furthermore it was judged that the result of the analysis on the sodium void reactivity .....
blanket. The standard analytical method for fast reactors has been applied, which was used for the JUPITER and other experimental analyses. Due to the lack of the analytical data the 2D RZ core calculation was mainly used. The 3D XYZ core calculation was applied only for the preliminary evaluation. Further in terms of the utilization of the BFS experimental analysis data for the standard data base for FBR core design, consistency evaluation with JUPITER experimental analysis data has been performed using the cross-section adjustment method. As the result of analyses, good agreement was obtained between calculations and experiments for the criticality and the reaction rate ratio. However, it was found that accurate evaluation of the reaction rate distribution was impossible without exact consideration of the arrangement of the two types of sodium (with and without hydrogen impurity), which can be accommodated by the 3D core analysis, thus it was essentia1. In addition, it was clarifie that there was a room for an improvement of the result on the reaction rate distribution in the blanket and shielding regions. The application of the 3D core calculation improved the result on the control rod worth because 3D core model can more exactly consider the shape of the control rod. Furthermore it was judged that the result of the analysis on the sodium void reactivity .....
Committee for the Joint Research Project on Backend Chemistry; Committee for the Collaborative Research on the Advanced Radiation Technology
JAERI-Conf 2000-009, 205 Pages, 2000/06
no abstracts in English
Mori, Koji*; Neyama, Atsushi*; Nakagawa, Koichi*
JNC TJ8400 2000-064, 175 Pages, 2000/03
In this study, the following tasks have been performed in order to evaluate the stability of earthquake resistance for the engineered barrier system(EBS) of High Level Waste (HLW) geological isolation system. (1)validation studies for the liquefaction model. The function of single-phase analysis without interaction between soil and pore water in three-dimensional effective stress analysis code, which had been developed in this study, have been verified using by actual vibration test data. This fiscal year, some validation studies for the function of liquefaction analysis was conducted usig by actual measured data through the laboratory liquefaction test. (2)Supplemental Studies for JNC Second Progress Report. Through the JNC second progress report, it was considered that the stability of earthquake resistance of the engineered barrier system would be maintained under the major seismic event. At the same time we have recognized that several model parameters for joint-crack element, which takes into account for the response behavior of material discontinuous surface such as between overpack and buffer material, will become important in the response behavior of the whole EBS. This year, we have studied about several topics, which arise from technical discussion on JNC second progress report and we have discussed about total seismic stability of EBS. (3)Supplemental Studies for joint study with NRIDP. At this fiscal year, the joint study with National Research Institute for Disaster Prevention (NRIDP) will be final stage. UP to this day, incremental validation studies had been continued using by mesuared data obtained from vibration test. In this final stage, validation analysis has been conducted again using by current version new analysis code and maintained the validation data which will be contribute to the joint study mentioned above.
Amemiya, Kiyoshi*; TRAN DUC PHI OAN*; Yamashita, Ryo*
JNC TJ8400 2000-056, 487 Pages, 2000/02
JNC presented the 2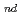 progressive reports on HLW disposal system. The documents impressed the importance of developing the engineering procedures and the model evaluating the thermo-hydro-mechanical phenomena in waste disposal system. In this research, the methods filling the gap between buffer and rock or buffer and overpack were examined. Bentonite pellets were tested as the filling materials. In order to assess the full-scale system performance, the Japanese experiences of buffer mass experiments were compared with the Prototype Repository Project of SKB in Sweden. Father more, the thermo-hydro-mechanical (THM) code named TRAMES was validated at the international co-research programs of DECOVALEX II.
progressive reports on HLW disposal system. The documents impressed the importance of developing the engineering procedures and the model evaluating the thermo-hydro-mechanical phenomena in waste disposal system. In this research, the methods filling the gap between buffer and rock or buffer and overpack were examined. Bentonite pellets were tested as the filling materials. In order to assess the full-scale system performance, the Japanese experiences of buffer mass experiments were compared with the Prototype Repository Project of SKB in Sweden. Father more, the thermo-hydro-mechanical (THM) code named TRAMES was validated at the international co-research programs of DECOVALEX II.
Amemiya, Kiyoshi*; TRAN DUC PHI OAN*; Yamashita, Ryo*
JNC TJ8400 2000-055, 49 Pages, 2000/02
JNC presented the 2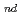 progressive reports on HLW disposal system. The documents impressed the importance of developing the engineering procedures and the model evaluating the thermo-hydro-mechanical phenomena in waste disposal system. In this research, the methods filling the gap between buffer and rock or buffer and overpack were examined. Bentonite pellets were tested as the filling materials. In order to assess the full-scale system performance, the Japanese experiences of buffer mass experiments were compared with the Prototype Repository Project of SKB in Sweden. Father more, the thermo-hydro-mechanical (THM) code named THAMES was validated at the international co-research programs of DECOVALEX II.
progressive reports on HLW disposal system. The documents impressed the importance of developing the engineering procedures and the model evaluating the thermo-hydro-mechanical phenomena in waste disposal system. In this research, the methods filling the gap between buffer and rock or buffer and overpack were examined. Bentonite pellets were tested as the filling materials. In order to assess the full-scale system performance, the Japanese experiences of buffer mass experiments were compared with the Prototype Repository Project of SKB in Sweden. Father more, the thermo-hydro-mechanical (THM) code named THAMES was validated at the international co-research programs of DECOVALEX II.
;
JAERI-Conf 99-010, p.98 - 0, 1999/10
no abstracts in English
Hunter
PNC TN9410 98-015, 81 Pages, 1998/02
The study was carried out within the framework of the PNC-CEA collaboration agreement. Data were provided, by CEA, for an experimental loading of a start-up core in Super-Phenix. This data was used at PNC to produce core flux snapshot calculations. CEA undertook a comparison of the PNC results with the equivalent calculations carried out by CEA, and also with experimental measurements from SPX. The resu1ts revealed a systematic radial flux tilt between the calculations and the reactor measurements, with the PNC tilts only  30-401 of those from CEA. CEA carried out an analysis of the component causes of the radial tilt. It was concluded that a major cause of radia1 tilt differences between the PNC and CEA calculations lay in the nuclear datasets used: JENDL-3.2 and CARNAVAL IV. For the final stage of the study, PNC undertook a sensitivity analysis, to examine the detailed differences between the two sets of nuclear data. The PNC flux calculations modelled SPX in both 2D (RZ) and 3D (hex-Z) geometries, using the diffusion programs CITATION and MOSES. The sensitivity analysis of the differences between the JENDL-3.2 and CARNAVAL IV nuclear datasets used the SAGEP calculational route. Both datasets were condensed to a single, non-standard, set of energy group boundaries. There were some incompatibilities in the cross-section formats of the two datasets. The sensitivity analysis showed that a relatively small number of nuclear data items contributed the bulk of the radial tilt difference between calculations with JENDL-3.2 and with CARNAVAL IV. A direct comparison between JENDL-3.2 and CARNAVAL IV data revealed the following. The Nu values showed little difference (<5|%). The only large fission cross-section differences were at low energy (<30% otherwise, with <10% typical). Although down-scattering reactions showed some large fractional differences, absolute differences were negligible compared with in-group scattering; for in-group scattering fractional ...
30-401 of those from CEA. CEA carried out an analysis of the component causes of the radial tilt. It was concluded that a major cause of radia1 tilt differences between the PNC and CEA calculations lay in the nuclear datasets used: JENDL-3.2 and CARNAVAL IV. For the final stage of the study, PNC undertook a sensitivity analysis, to examine the detailed differences between the two sets of nuclear data. The PNC flux calculations modelled SPX in both 2D (RZ) and 3D (hex-Z) geometries, using the diffusion programs CITATION and MOSES. The sensitivity analysis of the differences between the JENDL-3.2 and CARNAVAL IV nuclear datasets used the SAGEP calculational route. Both datasets were condensed to a single, non-standard, set of energy group boundaries. There were some incompatibilities in the cross-section formats of the two datasets. The sensitivity analysis showed that a relatively small number of nuclear data items contributed the bulk of the radial tilt difference between calculations with JENDL-3.2 and with CARNAVAL IV. A direct comparison between JENDL-3.2 and CARNAVAL IV data revealed the following. The Nu values showed little difference (<5|%). The only large fission cross-section differences were at low energy (<30% otherwise, with <10% typical). Although down-scattering reactions showed some large fractional differences, absolute differences were negligible compared with in-group scattering; for in-group scattering fractional ...
Takahashi, Tomoyuki
Purazuma, Kaku Yugo Gakkai-Shi, 73(12), p.1361 - 1362, 1997/12
no abstracts in English
Takemura, Morio*
PNC TJ9055 97-001, 112 Pages, 1997/03
With use of a standard groupwise shielding design library JSSTDL produced from the latest evaluated nuclear data library JENDL-3.2, experimental analyses for the Axial Shield Experiment (homogeneous and central blockage type shield configurations with B C or stainless steel shield material) were performed. The results were compared with those obtained by the same analysis method and input data using JSDJ2 library that had been applied consistently to the JASPER experiment analyses. In general, the results with JSSTDL analyses are higher than those by JSDJ2 as were found in analyses in last year for the Radial Shield Attenuation Experiment and the Special Materials Experiment. Consideration was made on the discrepancies between JSSTDL and JSDJ2 analysis results of the Axial Shield Experiment and also those of the sodium configulation in the Radial Shield Attenuation Experiment. The former was done by exchange of macro cross section of each region, and the latter forcused on sodium cross section was done with use of cross section sensitivity analysis method. Compilation of the input data necessary for future reanalyses of important configurations in JASPER experiments, that were selected in previous study in last year, were continued and new data were added into the computer disk holding previous ones.
C or stainless steel shield material) were performed. The results were compared with those obtained by the same analysis method and input data using JSDJ2 library that had been applied consistently to the JASPER experiment analyses. In general, the results with JSSTDL analyses are higher than those by JSDJ2 as were found in analyses in last year for the Radial Shield Attenuation Experiment and the Special Materials Experiment. Consideration was made on the discrepancies between JSSTDL and JSDJ2 analysis results of the Axial Shield Experiment and also those of the sodium configulation in the Radial Shield Attenuation Experiment. The former was done by exchange of macro cross section of each region, and the latter forcused on sodium cross section was done with use of cross section sensitivity analysis method. Compilation of the input data necessary for future reanalyses of important configurations in JASPER experiments, that were selected in previous study in last year, were continued and new data were added into the computer disk holding previous ones.
PNC TN8410 94-269, 77 Pages, 1994/07
This report describes FracMan discrete fracture flow transport modelling of the LPT-2, large-scale pumping and tracer test, at the SKB Aspo Hard Rock Laboratory. This work was carried out under the international cooperation program of the AsPo Task Force on Groundwater Flow and Transport of Solutes. The scale of simulation was approximately a one-kilometer cube. The discrete fracture model contains two major fracture types - fracture zones, which were located deterministically according to SKB's conceptual model of the Aspo site, and fractures outside the fracture zones which were generated stochastically. The geometric and hydraulic properties of each group were developed from the SKB modeling database, except for non-zone fracture length which we developed from our own mapping of surface outcrops. Two separate models were prepared for the March and September, 1993, task force meetings respectively. The March model represented the fracture zones as 10-m thick Planar regions containing populations of 30-m radius discrete fractures. The September model represented the fracture zones as single planes, which were discretized on a 20- to 30-m scale for a geostatistical assignment of properties. The September model also included conditioning of the properties to the borehole data. Both models generally reproduce the drawdown and transient pressure interference responses of the experiment. The tracer breakthroughs were simulated using only the September model. Calibration runs of the transport model varied the mean transport aperture, aperture variance, and aperture correlation length. The results of this modelling exercise show that a discrete fracture model can be applied at kilometer scales if the flow is dominated by a small portion of fracture population. The results also show that the SKB conceptual model is consistent with the field measurements.